For Application Developers
Geometry
|
|
Geant4 User's Guide
For Application Developers Geometry |
G4AssemblyVolume is a helper class which allows several logical volumes to be combined together in an arbitrary way in 3D space. The result is a placement of a normal logical volume, but where final physical volumes are many.
However, an assembly volume does not act as a real mother volume, being an envelope for its daughter volumes. Its role is over at the time the placement of the logical assembly volume is done. The physical volume objects become independent copies of each of the assembled logical volumes.
This class is particularly useful when there is a need to create a regular pattern in space of a complex component which consists of different shapes and can't be obtained by using replicated volumes or parametrised volumes (see also figure 4.1.2). Careful usage of G4AssemblyVolume must be considered though, in order to avoid cases of "proliferation" of physical volumes all placed in the same mother.

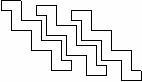
|
|
Figure 4.1.2 Examples of assembly of volumes. |
Filling an assembly volume with its "daughters"
Participating logical volumes are represented as a triplet of <logical
volume, translation, rotation> (G4AssemblyTriplet class).
The adopted approach is to place each participating logical volume with
respect to the assembly's coordinate system, according to the specified
translation and rotation.
Assembly volume placement
An assembly volume object is composed of a set of logical volumes; imprints of it can be made inside a mother logical volume.
Since the assembly volume class generates physical volumes during each
imprint, the user has no way to specify identifiers for these. An
internal counting mechanism is used to compose uniquely the names of the
physical volumes created by the invoked MakeImprint(...) method(s).
The name for each of the physical volume is generated with the following
format:
av_WWW_impr_XXX_YYY_ZZZ
where:
Destruction of an assembly volume
At destruction all the generated physical volumes and associated rotation
matrices of the imprints will be destroyed. A list of physical volumes created
by MakeImprint() method is kept, in order to be able to cleanup the objects
when not needed anymore. This requires the user to keep the assembly objects in
memory during the whole job or during the life-time of the G4Navigator,
logical volume store and physical volume store may keep pointers to physical
volumes generated by the assembly volume.
The MakeImprint() method will operate correctly also on transformations
including reflections and can be applied also to recursive assemblies (i.e., it
is possible to generate imprints of assemblies including other assemblies).
Giving true as the last argument of the MakeImprint() method,
it is possible to activate the volumes overlap check for the assembly's
constituents (the default is false).
At destruction of a G4AssemblyVolume, all its generated physical
volumes and rotation matrices will be freed.
Example
This example shows how to use the G4AssemblyVolume class. It implements a layered detector where each layer consists of 4 plates.
In the code below, at first the world volume is defined, then solid
and logical volume for the plate are created, followed by the definition of
the assembly volume for the layer.
The assembly volume for the layer is then filled by the plates in the same
way as normal physical volumes are placed inside a mother volume.
Finally the layers are placed inside the world volume as the imprints
of the assembly volume (see source listing 4.1.7).
static unsigned int layers = 5;
void TstVADetectorConstruction::ConstructAssembly()
{
// Define world volume
G4Box* WorldBox = new G4Box( "WBox", worldX/2., worldY/2., worldZ/2. );
G4LogicalVolume* worldLV = new G4LogicalVolume( WorldBox, selectedMaterial, "WLog", 0, 0, 0);
G4VPhysicalVolume* worldVol = new G4PVPlacement(0, G4ThreeVector(), "WPhys", worldLV, 0, false, 0);
// Define a plate
G4Box* PlateBox = new G4Box( "PlateBox", plateX/2., plateY/2., plateZ/2. );
G4LogicalVolume* plateLV = new G4LogicalVolume( PlateBox, Pb, "PlateLV", 0, 0, 0 );
// Define one layer as one assembly volume
G4AssemblyVolume* assemblyDetector = new G4AssemblyVolume();
// Rotation and translation of a plate inside the assembly
G4RotationMatrix Ra;
G4ThreeVector Ta;
// Rotation of the assembly inside the world
G4RotationMatrix Rm;
// Fill the assembly by the plates
Ta.setX( caloX/4. ); Ta.setY( caloY/4. ); Ta.setZ( 0. );
assemblyDetector->AddPlacedVolume( plateLV, G4Transform3D(Ta,Ra) );
Ta.setX( -1*caloX/4. ); Ta.setY( caloY/4. ); Ta.setZ( 0. );
assemblyDetector->AddPlacedVolume( plateLV, G4Transform3D(Ta,Ra) );
Ta.setX( -1*caloX/4. ); Ta.setY( -1*caloY/4. ); Ta.setZ( 0. );
assemblyDetector->AddPlacedVolume( plateLV, G4Transform3D(Ta,Ra) );
Ta.setX( caloX/4. ); Ta.setY( -1*caloY/4. ); Ta.setZ( 0. );
assemblyDetector->AddPlacedVolume( plateLV, G4Transform3D(Ta,Ra) );
// Now instantiate the layers
for( unsigned int i = 0; i < layers; i++ )
{
// Translation of the assembly inside the world
G4ThreeVector Tm( 0,0,i*(caloZ + caloCaloOffset) - firstCaloPos );
assemblyDetector->MakeImprint( worldLV, G4Transform3D(Tm,Rm) );
}
}
|
|
Source listing 4.1.7 An example of usage of the G4AssemblyVolume class. |
The resulting detector will look as in figure 4.1.3, below:
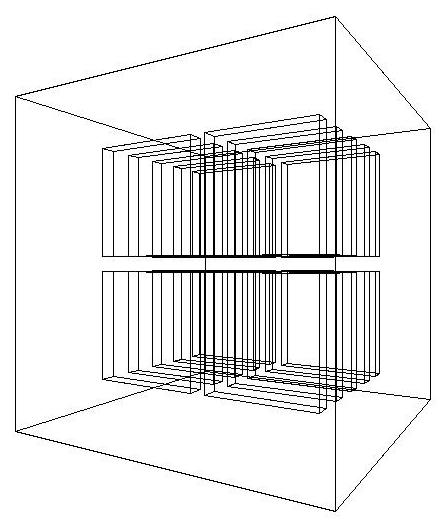 |
|
Figure 4.1.3 The geometry corresponding to source listing 4.1.7. |